Pivot points are one of the most popular tools for intraday forex trading. They provide traders with key levels of support and resistance based on the previous trading session’s high, low, and close. These levels help traders identify potential price reversals, breakouts, and optimal entry and exit points. By integrating pivot points into your trading strategy, you can gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics and make more informed decisions.
In this blog, we’ll explore how to use pivot points for intraday forex trading, covering their calculation, significance, and application in real-world scenarios.
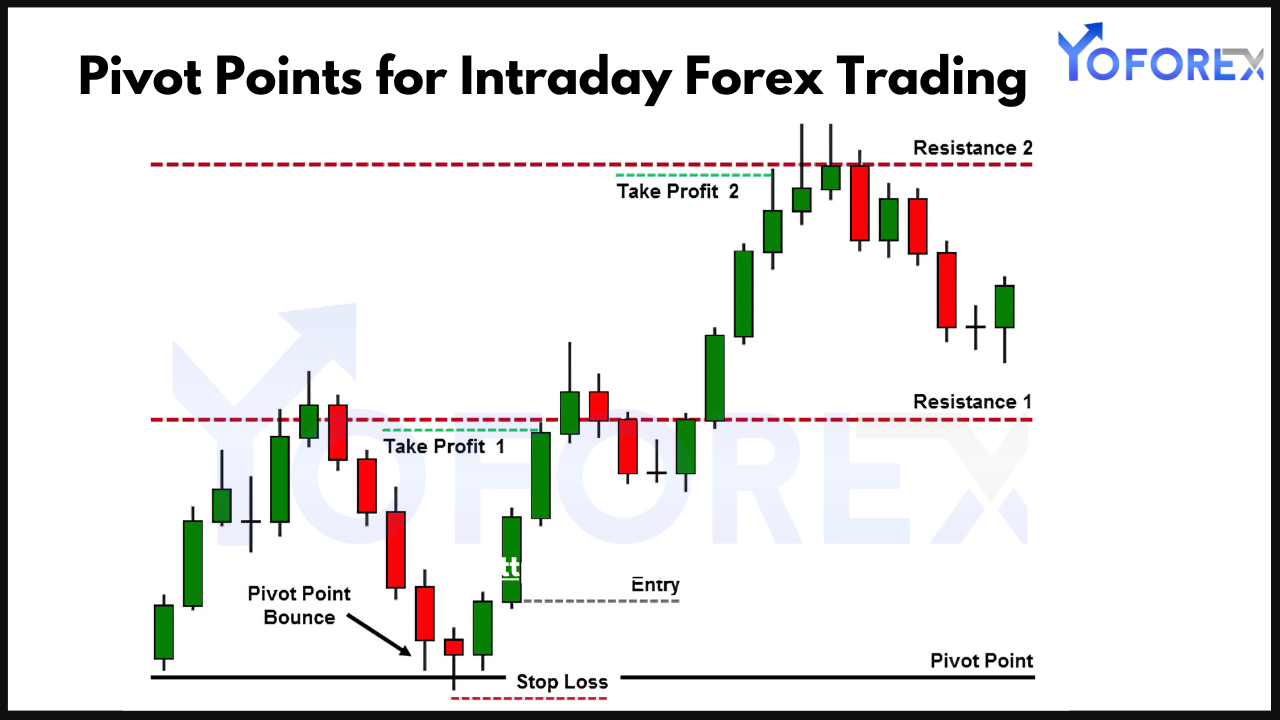
What Are Pivot Points?
Pivot points are calculated levels on a price chart that indicate potential turning points in the market. These levels include the central pivot point (PP), support levels (S1, S2, S3), and resistance levels (R1, R2, R3). Pivot points are derived from the previous trading session’s data and are particularly useful for intraday traders looking to capitalize on short-term price movements.
How to Calculate Pivot Points
The standard pivot point formula is straightforward:
Pivot Point (PP) = (High + Low + Close) / 3
From the central pivot point, support and resistance levels are calculated as follows:
- Resistance 1 (R1) = (2 × PP) – Low
- Resistance 2 (R2) = PP + (High – Low)
- Resistance 3 (R3) = High + 2 × (PP – Low)
- Support 1 (S1) = (2 × PP) – High
- Support 2 (S2) = PP – (High – Low)
- Support 3 (S3) = Low – 2 × (High – PP)
Some trading platforms calculate these levels automatically, saving traders the effort of manual computation.
Why Use Pivot Points in Forex Trading?
Pivot points are highly regarded for several reasons:
- Objectivity:
- Pivot points are based on concrete mathematical formulas, reducing the subjectivity associated with other technical indicators.
- Ease of Use:
- Once calculated, pivot points remain constant throughout the trading day, providing clear reference points.
- Market Insight:
- These levels often align with significant price action areas, offering insights into market sentiment and potential reversals.
- Versatility:
- Pivot points work across all timeframes and currency pairs, making them a versatile tool for intraday traders.
How to Use Pivot Points in Intraday Trading
1. Identify Key Levels
Start by plotting the pivot point, support, and resistance levels on your chart. These levels act as potential turning points or breakout zones:
- PP: Serves as the main level to gauge market sentiment.
- S1, S2, S3: Act as potential support levels.
- R1, R2, R3: Serve as potential resistance levels.
2. Determine Market Sentiment
- Above PP: If the price is trading above the pivot point, it suggests bullish sentiment, and traders may look for buying opportunities.
- Below PP: If the price is trading below the pivot point, it indicates bearish sentiment, and traders may look for selling opportunities.
3. Trade Reversals
Pivot points often act as support or resistance levels where price reversals occur. For reversal trades:
- Look for price to test and fail to break a pivot level (e.g., R1 or S1).
- Confirm the reversal with candlestick patterns, such as pin bars or engulfing candles.
- Enter a trade in the opposite direction, setting stop-loss orders just beyond the pivot level.
4. Trade Breakouts
When the price breaks through a pivot level with strong momentum, it often signals a continuation of the trend. For breakout trades:
- Wait for a clean break above resistance (e.g., R1) or below support (e.g., S1).
- Confirm the breakout with high trading volume or momentum indicators like the RSI or MACD.
- Enter the trade and set targets at the next pivot level (e.g., R2 or S2).
5. Use Pivot Points with Other Indicators
Pivot points are more effective when combined with other technical indicators. For example:
- Moving Averages: Use moving averages to identify the overall trend and align pivot point trades with the trend.
- RSI: Look for overbought or oversold conditions near pivot levels to confirm reversals.
- Bollinger Bands: Use Bollinger Bands to assess volatility and pinpoint breakout opportunities.
Practical Example of Using Pivot Points
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario with the EUR/USD currency pair:
- Setup:
- The previous day’s high was 1.1050, low was 1.1000, and close was 1.1025.
- Pivot point (PP) = (1.1050 + 1.1000 + 1.1025) / 3 = 1.1025
- R1 = (2 × 1.1025) – 1.1000 = 1.1050
- S1 = (2 × 1.1025) – 1.1050 = 1.1000
- Analysis:
- The price opens near the PP at 1.1025 and begins to rise toward R1 at 1.1050.
- The price tests R1 but fails to break through, forming a bearish pin bar.
- Trade Execution:
- Enter a short trade at 1.1045, anticipating a reversal back to the PP level.
- Set a stop-loss at 1.1060, just above R1.
- Set a take-profit target at 1.1020, slightly above the PP level.
- Outcome:
- The price reverses and hits the take-profit target, completing a successful trade.
Advantages of Using Pivot Points
- Simplicity:
- Pivot points are easy to calculate and interpret, making them accessible to traders of all skill levels.
- Relevance Across Markets:
- They are widely used by institutional and retail traders, adding credibility to these levels.
- Adaptability:
- Work well in trending, range-bound, and volatile markets.
- Clear Reference Points:
- Provide predefined levels for planning trades and managing risk.
Challenges and Limitations
- False Breakouts:
- Prices may temporarily breach pivot levels before reversing, leading to potential losses.
- Lagging Nature:
- Pivot points are based on historical data and may not fully reflect real-time market conditions.
- Market-Specific Variability:
- The effectiveness of pivot points can vary across currency pairs and market sessions.
Tips for Effective Pivot Point Trading
- Use Higher Timeframes for Context:
- Analyze daily or weekly pivot points to understand the broader trend.
- Combine with Fundamental Analysis:
- Monitor economic events that could impact price movements around pivot levels.
- Practice Patience:
- Wait for confirmation before entering trades, especially around key levels.
- Adapt to Market Conditions:
- In volatile markets, use wider stop-loss levels to account for larger price swings.
Conclusion
Pivot points are a powerful tool for intraday forex trading, offering traders a structured approach to identifying key levels of support and resistance. By understanding how to calculate and use pivot points effectively, you can improve your ability to spot trading opportunities and manage risk.
However, like any trading tool, pivot points are most effective when used in conjunction with other technical indicators and a solid risk management strategy. With practice and discipline, pivot points can become an integral part of your trading arsenal, helping you navigate the forex market with confidence.

