Elliott Wave Theory is a widely respected method of technical analysis that provides insight into market behavior by identifying repetitive patterns in price movements. Named after its founder Ralph Nelson Elliott, the theory is particularly popular among forex traders due to its ability to forecast market trends and reversals. This blog explores how Elliott Wave Theory applies to forex markets, its fundamental principles, and how traders can use it to enhance their trading strategies.
Understanding Elliott Wave Theory
At its core, Elliott Wave Theory is based on the idea that financial markets move in predictable waves influenced by collective trader psychology. These waves are characterized by alternating phases of optimism and pessimism, creating cycles that repeat over time.
The Two Types of Waves:
- Impulse Waves:
- Impulse waves consist of five sub-waves that move in the direction of the larger trend. These waves are labeled as 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
- Among these, Wave 3 is often the strongest and most extended.
- Corrective Waves:
- Corrective waves consist of three sub-waves that move against the larger trend. These waves are labeled as A, B, and C.
- Corrective waves typically represent a pause or retracement in the prevailing trend.
Together, these impulse and corrective waves form the basis of the Elliott Wave Theory and help traders identify the overall market structure.
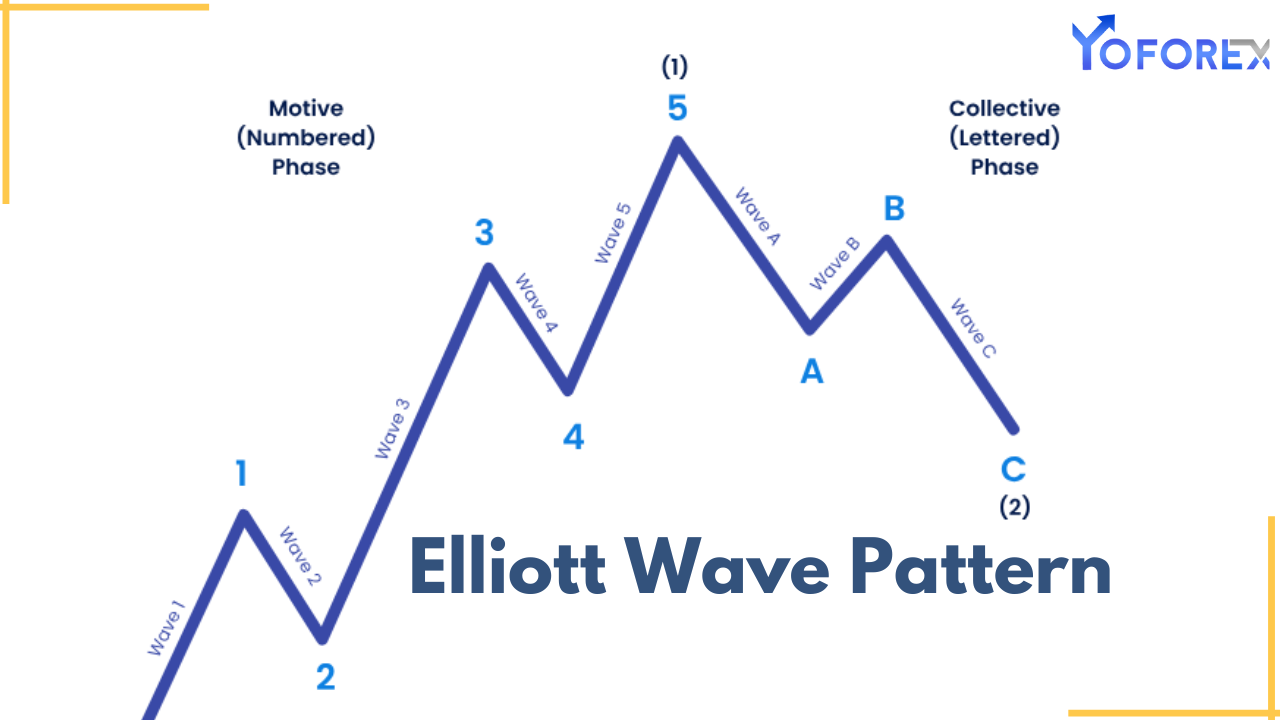
Elliott Wave Structure in Forex Markets
In forex trading,the Elliott Wave Theory is particularly useful because of the highly liquid and volatile nature of currency pairs. Price movements in forex often exhibit the patterns described by Elliott, making it an effective tool for predicting market behavior.
- Wave Patterns in Trending Markets:
- In an uptrend, impulse waves move higher, followed by corrective waves that pull back. The overall structure consists of five upward waves (impulse) and three downward waves (correction).
- In a downtrend, impulse waves move lower, with corrective waves retracing upward.
- Wave Patterns in Consolidating Markets:
- Forex markets often experience periods of consolidation, during which corrective waves dominate. Identifying these patterns helps traders anticipate breakout or trend continuation opportunities.
How to Identify Elliott Waves in Forex Charts
- Determine the Trend:
- Start by analyzing the larger time frame (e.g., daily or weekly) to identify the primary trend direction.
- Look for higher highs and higher lows in an uptrend or lower highs and lower lows in a downtrend.
- Count the Waves:
- Use smaller time frames to count the sub-waves within the larger trend.
- Ensure that the wave count aligns with the five-wave impulse and three-wave corrective structure.
- Follow the Rules and Guidelines:
- Wave 2 cannot retrace more than 100% of Wave 1.
- Wave 3 is never the shortest among Waves 1, 3, and 5.
- Wave 4 should not overlap the price territory of Wave 1.
- Validate with Fibonacci Ratios:
- Elliott Wave Theory often incorporates Fibonacci retracement and extension levels to validate wave counts. For example:
- Wave 2 typically retraces 50%-61.8% of Wave 1.
- Wave 3 often extends to 161.8% of Wave 1.
- Wave 4 usually retraces 38.2%-50% of Wave 3.
- Elliott Wave Theory often incorporates Fibonacci retracement and extension levels to validate wave counts. For example:
Practical Applications of Elliott Wave Theory in Forex
- Trend Identification:
- Traders can use Elliott Wave Theory to determine whether the market is trending or consolidating, enabling them to align their strategies with prevailing market conditions.
- Entry and Exit Points:
- By identifying specific waves, traders can time their entries and exits more effectively. For instance:
- Entering during the start of Wave 3 in an uptrend offers a high-probability trade.
- Exiting at the end of Wave 5 allows traders to capture maximum trend movement.
- By identifying specific waves, traders can time their entries and exits more effectively. For instance:
- Risk Management:
- Understanding corrective wave structures helps traders set stop-loss levels. For example, placing a stop-loss below the start of Wave 1 in an uptrend provides a logical point of protection.
- Forecasting Future Price Movements:
- By analyzing completed waves, traders can predict the next wave’s direction and potential targets, providing a roadmap for future price action.
Challenges of Using Elliott Wave Theory in Forex
- Subjectivity in Wave Counting:
- Accurately identifying and counting waves can be challenging, especially in complex market conditions. Traders may interpret the same price action differently.
- Requires Experience:
- Mastering Elliott Wave Theory takes time and practice. Beginners may struggle with its nuances and intricacies.
- Dependence on Other Indicators:
- While Elliott Wave Theory is powerful, it is most effective when combined with other technical tools, such as Fibonacci levels, moving averages, or momentum indicators.
Tips for Applying Elliott Wave Theory Successfully
- Start Simple:
- Focus on identifying the primary trend and the most apparent waves before delving into complex patterns.
- Use Multiple Time Frames:
- Analyze larger time frames for overall trends and smaller time frames for precise wave counts.
- Combine with Other Analysis Tools:
- Use support and resistance levels, Fibonacci retracements, or RSI to confirm wave patterns and improve accuracy.
- Practice on Historical Data:
- Backtest your wave counts on historical charts to build confidence and refine your skills.
- Be Flexible:
- The market does not always follow Elliott Wave rules perfectly. Be prepared to adapt your wave counts as new data emerges.
Real-Life Example: Applying Elliott Wave Theory to EUR/USD
Let’s consider a hypothetical application of Elliott Wave Theory to the EUR/USD currency pair:
- Identifying the Trend:
- On the daily chart, EUR/USD is in an uptrend, with higher highs and higher lows.
- Counting the Waves:
- A five-wave impulse structure is observed:
- Wave 1: Initial rally from 1.1000 to 1.1200.
- Wave 2: Retracement to 1.1100 (50% of Wave 1).
- Wave 3: Strong rally to 1.1500, extending 161.8% of Wave 1.
- Wave 4: Consolidation to 1.1400 (38.2% of Wave 3).
- Wave 5: Final push to 1.1600.
- A five-wave impulse structure is observed:
- Using Fibonacci Levels:
- Wave 2 retracement aligns with the 50% Fibonacci level, and Wave 3 extension reaches the 161.8% level, validating the wave count.
- Planning Trades:
- Enter during the start of Wave 3 at 1.1100, with a target of 1.1500 and a stop-loss below 1.1000.
Conclusion
Elliott Wave Theory is a powerful analytical tool that enables forex traders to interpret market behavior and anticipate future price movements. By understanding its principles and applying them with discipline, traders can enhance their decision-making process and improve trading outcomes. However, like any strategy, Elliott Wave Theory requires practice, patience, and a willingness to adapt to changing market conditions.
Whether you are a novice or an experienced trader, incorporating Elliott Wave Theory into your forex trading toolkit can provide valuable insights and a competitive edge in the fast-paced world of currency markets.

