Forex trading is a dynamic market where traders aim to profit from fluctuations in currency prices. One of the critical concepts that every trader must understand is the “spread.” The forex spread is a seemingly simple metric, but it plays a significant role in determining your trading costs and profitability. This blog delves into the concept of forex spread, its types, how it impacts profits, and strategies to manage it effectively.
What is a Forex Spread?
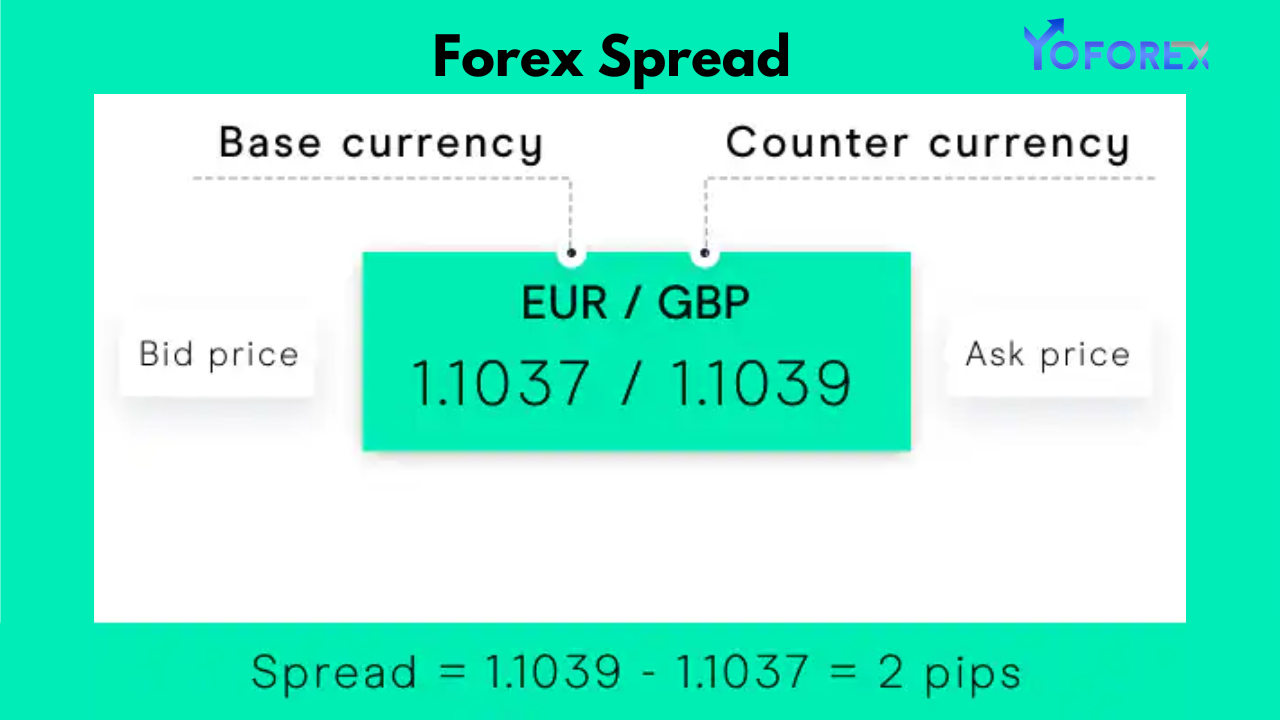
The forex spread is the difference between the bid price (the price at which you can sell a currency) and the asking price (the price at which you can buy a currency). It represents the cost of trading and is typically measured in pips, the smallest unit of price movement in forex trading.
Key Components:
- Bid Price: The highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a currency.
- Ask Price: The lowest price a seller is willing to accept for a currency.
- Spread: Ask Price – Bid Price.
Example:
- EUR/USD:
- Bid Price: 1.1200
- Ask Price: 1.1202
- Spread: 2 pips.
Types of Forex Spreads
Forex spreads can vary depending on the type of broker and market conditions. Understanding the different types of spreads can help traders choose the right broker and strategy.
1. Fixed Spreads
- Fixed spreads remain constant, regardless of market conditions.
- Offered by market maker brokers.
- Suitable for traders who prefer consistent costs.
Pros:
- Predictable trading costs.
- Ideal for beginners or low-volatility trading.
Cons:
- May be higher than variable spreads during normal market conditions.
2. Variable Spreads
- Variable spreads fluctuate based on market volatility and liquidity.
- Offered by ECN (Electronic Communication Network) or STP (Straight Through Processing) brokers.
Pros:
- Lower spreads during periods of high liquidity.
- Transparent pricing directly from the market.
Cons:
- Can widen significantly during news events or low liquidity periods.
Factors Influencing Forex Spreads
Spreads are not static; they are influenced by several factors:
1. Market Liquidity
- Major currency pairs like EUR/USD have lower spreads due to high liquidity.
- Exotic pairs like USD/TRY often have wider spreads because of lower trading volumes.
2. Market Volatility
- During high volatility, such as news releases, spreads can widen significantly.
- Example: Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) announcements often cause sudden spikes in spreads.
3. Broker Type
- Market makers may offer fixed spreads, while ECN brokers typically provide variable spreads.
4. Trading Session
- Spreads are narrower during active trading sessions (e.g., London and New York overlaps).
- Wider spreads are common during low activity periods, such as the Asian session.
How Forex Spreads Impact Profits
The spread is a direct cost of trading and influences your profitability in several ways:
1. Initial Cost of Entry
- When entering a trade, you immediately incur the cost of the spread.
- The price must move in your favor by at least the spread amount to reach breakeven.
Example:
- Spread: 3 pips.
- Trade size: 1 standard lot (100,000 units).
- Cost of Spread: $30.
2. Scalping and Day Trading
- High-frequency trading strategies like scalping are more sensitive to spreads.
- Wider spreads can erode profits from small price movements.
3. Impact on Risk-Reward Ratio
- Larger spreads can reduce the risk-reward ratio of a trade, making it less attractive.
- Example: A 10-pip target with a 3-pip spread leaves only 7 pips of net profit potential.
4. Effect on Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
- Wider spreads can cause trades to hit stop-loss levels prematurely or reduce the likelihood of reaching take-profit targets.
Managing Forex Spreads Effectively
Traders can mitigate the impact of spreads on their profitability with the following strategies:
1. Choose the Right Broker
- Compare brokers based on their spread offerings and account types.
- ECN brokers may offer lower spreads but charge a commission, while market makers provide fixed spreads without additional fees.
2. Trade During High-Liquidity Periods
- Focus on trading during major sessions (e.g., London and New York) when spreads are typically narrower.
3. Avoid Trading During High-Impact News Events
- Volatile news events can cause spreads to widen dramatically.
- Wait for spreads to stabilize before entering trades.
4. Monitor Spread Changes
- Use trading platforms that display live spread information.
- Adjust your strategy based on current spread conditions.
5. Optimize Position Sizing
- Calculate the cost of spreads relative to your position size and adjust accordingly.
6. Focus on Major Currency Pairs
- Major pairs like EUR/USD and USD/JPY generally have the lowest spreads due to high liquidity.
Tools for Spread Analysis
Several tools can help traders analyze and manage spreads:
1. Trading Platforms
- Platforms like MetaTrader and cTrader provide live spread data and customizable chart overlays.
2. Economic Calendars
- Monitor economic calendars to avoid trading during events that may cause spread spikes.
3. Spread Tracking Indicators
- Indicators like spread meters display real-time spread levels on charts.
Conclusion
Understanding forex spreads and their impact on trading is essential for optimizing profitability. Spreads represent a significant cost of trading, particularly for short-term strategies like scalping. By choosing the right broker, trading during high-liquidity periods, and monitoring spread fluctuations, traders can minimize costs and enhance their overall performance. In a market where every pip counts, mastering the nuances of forex spreads can make a substantial difference in achieving long-term success.

